Basic Scripting for Hackers: A Beginner’s Essential Guide
Category: Ethical Hacking
Unlock the Power of Basic Scripting for Hackers
Are you just stepping into the world of ethical hacking and wondering how to harness the true potential of scripting? Whether you’re a complete beginner struggling to understand how scripts can automate tasks and reveal system vulnerabilities or an aspiring hacker craving a solid foundation before advancing, this guide is crafted just for you. Basic scripting is the backbone of ethical hacking — it transforms manual processes into repeatable, efficient commands to explore, exploit, and secure systems. But with so many scripting languages and techniques out there, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed or unsure where to start.
This post is your roadmap through the essentials: from understanding scripts and their role in hacking, to hands-on tutorials on the most useful languages and scripts every ethical hacker should master. Unlike generic tutorials, this guide focuses on practical hacking applications, equipping you with real-world skills and insights often overlooked by broader programming content. We won’t just teach you syntax — we’ll show how scripting intersects with cyber attack methodologies and defense strategies.
By the end, you’ll be confident writing your own scripts tailored for hacking tasks, speeding up penetration tests, and uncovering vulnerabilities effectively. Ready to elevate your hacking skills with scripting? Keep reading and begin your journey from novice to capable ethical hacker, starting right here.
- Unlock the Power of Basic Scripting for Hackers
- Understanding the Role of Scripting in Ethical Hacking
- Overview of Popular Scripting Languages for Hackers
- Setting Up Your Scripting Environment: Installing Interpreters, Editors, and Configuring Your System for Ethical Hacking Scripts
- Basic Syntax and Programming Concepts for Beginners
- Writing Your First Ethical Hacking Script: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
- Automating Reconnaissance and Scanning Tasks: How to Script Network Scans, Port Checks, and Data Gathering to Save Time
- Practical Scripting Examples for Exploiting Vulnerabilities
- Debugging and Improving Your Scripts: Tools and Techniques to Troubleshoot and Refine Your Hacking Scripts Effectively
- Ethical and Legal Considerations When Using Scripts: Understanding Responsible Usage, Permission Requirements, and Avoiding Illegal Activities
- Next Steps: How to Advance Your Scripting Skills for Complex Hacking Tasks and Resources for Continued Learning
Understanding the Role of Scripting in Ethical Hacking
Scripting is a fundamental skill for ethical hackers, enabling the automation of repetitive tasks and the execution of complex operations that would be cumbersome or impossible to perform manually. At its core, scripting boosts hacking efficiency by allowing hackers to customize tools, rapidly scan networks, exploit vulnerabilities, and gather intelligence with precision and speed. Whether it’s writing a simple script to automate password guessing or developing a sophisticated payload to bypass security measures, scripts empower ethical hackers to stay ahead in the cybersecurity game.
Why Scripts Matter in Ethical Hacking
- Automation of Tedious Tasks: Manual processes like scanning IP ranges, checking for open ports, or scraping data from websites can be time-consuming. Scripting eliminates tedium by automating these tasks, leaving hackers more time to analyze results and develop strategies.
- Custom Exploits and Payloads: Off-the-shelf hacking tools are useful but limited. Scripting allows hackers to craft custom exploits tailored to specific systems, increasing the chance of successful penetration.
- Rapid Information Gathering: Instantaneously collect and process system information, helping hackers identify weaknesses faster and more efficiently.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: Scripts can be modified on the fly to adjust to different targets, security setups, or attack scenarios, making hacking efforts more dynamic and effective.
Common Uses of Scripting in Ethical Hacking
- Reconnaissance and Scanning: Automating network discovery, service enumeration, and vulnerability scanning using scripts reduces manual overhead.
- Brute Force Attacks: Writing scripts to execute password guessing attempts quickly and stealthily across multiple accounts or services.
- Exploitation: Deploying payloads and executing exploits tailored by scripts to bypass firewalls, antivirus, or intrusion detection systems.
- Post-Exploitation Tasks: Automating data extraction, privilege escalation, and persistence mechanisms on compromised systems.
- Reporting and Documentation: Generating structured reports from raw data collected during penetration tests to streamline communication with stakeholders.
By mastering scripting, ethical hackers gain a powerful toolkit that not only accelerates their workflow but also enhances the depth and precision of their security assessments. This makes scripting not just a technical skill—but a strategic advantage in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.

Image courtesy of Tima Miroshnichenko
Overview of Popular Scripting Languages for Hackers
Choosing the right scripting language is crucial for ethical hackers aiming to automate tasks, develop exploits, or analyze vulnerabilities efficiently. Among the many options available, Python, Bash, PowerShell, and JavaScript stand out as the most popular and versatile scripting languages in hacking scenarios. Each language offers unique advantages depending on the target environment, the type of attack, and the hacker’s skill level.
Python: The Go-To Language for Ethical Hackers
Python’s simplicity, readability, and extensive libraries make it the top choice for beginners and experts alike. It excels in automating tasks like reconnaissance, scanning, and exploitation through modules such as scapy (packet manipulation), socket (network connections), and requests (web interactions). Python’s powerful frameworks, including Metasploit integrations and Impacket, facilitate writing custom exploits and post-exploitation tools. Moreover, Python’s cross-platform compatibility allows scripts to run seamlessly on Windows, Linux, and macOS, making it indispensable for diverse hacking environments.
Bash: Master of Unix/Linux Shell Scripting
Bash scripting is fundamental for hackers working directly in Linux or Unix-based systems, where most servers and network devices run. Bash is perfect for automating system reconnaissance, setting up backdoors, and chaining together command-line tools like nmap, netcat, and grep into powerful attack pipelines. Its straightforward syntax and tight integration with operating system utilities enable rapid task execution without requiring additional installations. However, Bash is generally limited to Unix-like environments and is less suitable for Windows-centric attacks.
PowerShell: The Windows Penetration Tester’s Weapon
PowerShell is the preferred scripting language for Windows environments, capable of automating complex tasks and interacting deeply with the Windows operating system and Active Directory. Its advanced features allow ethical hackers to perform privilege escalation, lateral movement, and persistence through script-based payloads that evade common antivirus solutions. PowerShell’s access to .NET libraries and its ability to run remote commands via Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) make it a formidable tool for internal network hacking and red team exercises. For anyone targeting Windows infrastructure, mastering PowerShell scripting is essential.
JavaScript: The Web and Browser Exploitation Language
JavaScript plays a critical role in hacking scenarios centered around web applications and browser exploitation. It is widely used for crafting client-side payloads in cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, injecting malicious code into vulnerable web pages, or manipulating browser behavior during social engineering campaigns. With environments like Node.js, JavaScript can also be used for server-side scripting and building networked hacking tools. While less common for direct system exploitation, JavaScript’s relevance grows continuously as web technologies evolve and form a major attack surface.
Choosing between these languages depends heavily on the hacking context:
- Use Python for versatility and powerful automation.
- Use Bash when operating within Unix/Linux systems.
- Use PowerShell for Windows network penetration and internal attacks.
- Use JavaScript for web client and server-level exploits.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of these scripting languages empowers ethical hackers to select the best tool for every stage of a penetration test or red team engagement, boosting both efficiency and impact.
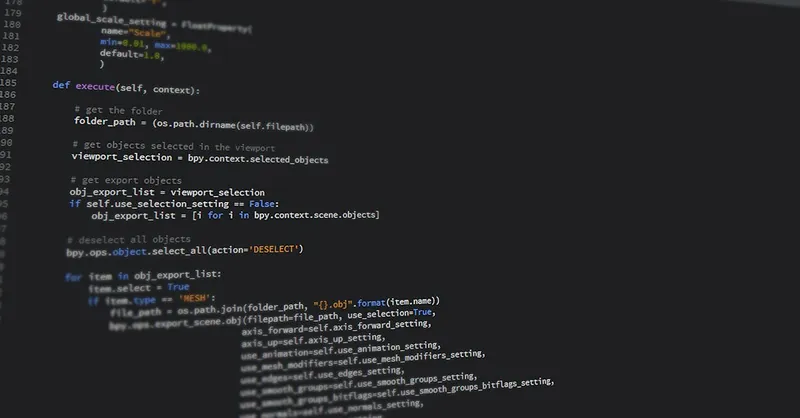
Image courtesy of Pixabay
Setting Up Your Scripting Environment: Installing Interpreters, Editors, and Configuring Your System for Ethical Hacking Scripts
Before diving into scripting for ethical hacking, setting up a reliable and efficient scripting environment is essential. This ensures you can write, test, and execute your scripts seamlessly, which is critical for rapid experimentation and learning. Whether you plan to use Python, Bash, PowerShell, or JavaScript, having the right tools installed and a well-configured system will drastically improve your workflow and effectiveness.
1. Installing Essential Interpreters and Runtimes
- Python: Download and install the latest version of Python from the official python.org website, ensuring you select the option to add Python to your system PATH. For ethical hacking, having package managers like
pipenables installing powerful libraries such asscapy,requests, andimpacket. - Bash: Unix and Linux systems come pre-installed with Bash by default, but Windows users can enable Bash through the Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). Installing WSL provides a native Linux environment on Windows, crucial for running many Bash scripts and Linux-based tools.
- PowerShell: Windows 10 and later versions come with PowerShell pre-installed. For expanded capabilities, especially cross-platform scripting, install the latest PowerShell Core version from GitHub’s PowerShell repository.
- JavaScript: For server-side JavaScript scripting, install Node.js from nodejs.org. This not only provides a JavaScript runtime but also gives access to npm (Node Package Manager), which is useful for installing hacking-related modules.
2. Choosing and Configuring Code Editors and IDEs
Selecting an efficient editor or integrated development environment (IDE) enhances script writing and debugging. Popular choices include:
- Visual Studio Code (VS Code): Offers extensive syntax highlighting, debugging tools, and plugins tailored for Python, JavaScript, and PowerShell. Its customizable terminal integrates well with system shells for real-time script testing.
- Sublime Text: Lightweight and fast, suitable for quick script edits and bash scripting.
- PyCharm: Ideal for Python scripting with advanced features like intelligent code completion and virtual environment management.
- Windows Terminal: For Windows users working with PowerShell and WSL, this modern terminal application supports multiple tabs and customized shells, improving multitasking.
3. System Configuration Tips for Optimal Scripting
- Enable Execution Permissions: On Unix/Linux systems, make your scripts executable by running
chmod +x scriptname.shfor Bash or Python files. Windows PowerShell scripts require execution policy adjustments via the commandSet-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSignedto allow running trusted scripts. - Setup Virtual Environments: Use Python virtual environments (
venvorvirtualenv) to isolate your hacking projects’ dependencies, preventing conflicts and maintaining clean environments. - Install Network Tools: Complement your scripting setup with essential command-line tools like
nmap,netcat, andtcpdumpto extend your scripts’ capabilities in reconnaissance and network analysis. - Configure Proxy and VPN Settings: For safe and anonymous testing, configure your environment to route traffic through proxies or VPNs, which can also help simulate attack conditions or bypass geo-restrictions during pen-tests.
By correctly installing interpreters, selecting versatile editors, and configuring your system for script execution and development, you establish a strong foundation for building powerful ethical hacking scripts. This preparation not only accelerates your scripting learning curve but also ensures a smoother transition into applying scripts effectively during penetration testing and cybersecurity research.
Image courtesy of luis gomes
Basic Syntax and Programming Concepts for Beginners
Before diving into complex hacking scripts, it’s essential to grasp the basic syntax and core programming concepts that form the foundation of any scripting language. Understanding these fundamentals will empower beginner ethical hackers to write effective, clean, and reusable code that automates tasks and exploits vulnerabilities strategically.
Variables: Storing and Manipulating Data
Variables are named containers that hold data values. In scripting, variables store crucial information such as IP addresses, port numbers, user inputs, or scan results. For example, in Python, you might write:
target_ip = "192.168.1.10"
port = 80
Here, target_ip and port are variables holding string and integer data respectively. Variables allow your script to flexibly handle and manipulate data during runtime.
Loops: Repeating Tasks Efficiently
Loops automate repetitive actions, which is indispensable when scanning multiple hosts or brute forcing passwords. The two common types are:
- For loops: Iterate over a sequence or range.
python
for port in range(1, 1025):
print(f"Scanning port: {port}")
- While loops: Repeat as long as a condition holds true.
python
attempts = 0
while attempts < 5:
print("Trying password guess...")
attempts += 1
Loops speed up tedious hacking tasks by automating repeated operations.
Conditionals: Decision Making in Scripts
Conditionals enable your script to make decisions based on certain criteria, branching code execution accordingly. This is particularly useful when checking if a port is open or a login attempt is successful.
Example in Python:
if response_code == 200:
print("Target is reachable")
else:
print("Target is down or unreachable")
By implementing conditionals, your script can handle varying scenarios dynamically.
Functions: Organizing and Reusing Code
Functions are blocks of reusable code designed to perform specific tasks, making your scripts modular and easier to manage. For hackers, functions help encapsulate common actions such as scanning a host or sending a payload.
Basic function example:
def scan_port(ip, port):
# code to scan a port
print(f"Scanning {ip} on port {port}")
scan_port("192.168.1.10", 80)
Functions improve readability and facilitate complex scripting workflows in penetration tests.
Hacker-Friendly Example: Automating a Basic Port Scan
Putting these concepts together, here is a sample Python snippet demonstrating variables, loops, conditionals, and functions tailored for ethical hacking:
def scan_port(ip, port):
# Simplified example: pretend to scan a port
print(f"Scanning {ip} on port {port}")
# Imagine a check here; let's say port 80 is open
if port == 80:
return True
else:
return False
target_ip = "192.168.1.10"
for port in range(75, 85):
if scan_port(target_ip, port):
print(f"Port {port} is open!")
else:
print(f"Port {port} is closed.")
This basic script automates scanning ports 75 through 84 on a target IP address, printing the status of each port. Mastering such foundational programming concepts is the gateway to developing more sophisticated scripts that can power real-world ethical hacking engagements.
Image courtesy of luis gomes
Writing Your First Ethical Hacking Script: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
Now that you understand the basic syntax and core programming concepts, it's time to apply this knowledge by writing your very first ethical hacking script. In this tutorial, we will create a simple reconnaissance script in Python that performs a basic network scan to detect active hosts within an IP range. Reconnaissance is a critical phase in ethical hacking, helping you gather vital information about targets before launching further penetration testing activities.
What This Script Will Do
- Accept a range of IP addresses from the user
- Ping each IP address to check if the host is alive
- Display a list of responsive hosts found in the scan
This approach introduces you to network scanning automation, showing how Python can facilitate fast and efficient information gathering crucial for hacking investigations.
Step 1: Import Required Libraries
We need to leverage Python’s built-in subprocess module to send ping requests, and ipaddress for handling IP ranges safely.
import subprocess
import ipaddress
Step 2: Define a Function to Ping Hosts
Create a function ping_host that sends a ping command to a target IP and returns whether the host is reachable.
def ping_host(ip):
# '-c 1' sends one ping packet (Linux/macOS). Use '-n 1' for Windows.
command = ['ping', '-c', '1', str(ip)]
try:
output = subprocess.run(command, stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
if output.returncode == 0:
return True
else:
return False
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error pinging {ip}: {e}")
return False
Step 3: Scan an IP Range
Ask the user to input a network in CIDR notation like "192.168.1.0/28". Use ipaddress.IPv4Network to expand this range, then call ping_host on each IP.
def scan_network():
network_input = input("Enter the network (e.g., 192.168.1.0/28): ")
try:
network = ipaddress.IPv4Network(network_input, strict=False)
except ValueError:
print("Invalid network format. Please try again.")
return
live_hosts = []
print(f"Scanning network: {network}")
for ip in network.hosts():
if ping_host(ip):
print(f"Host {ip} is alive")
live_hosts.append(str(ip))
print("\nScan complete. Live hosts:")
for host in live_hosts:
print(host)
Step 4: Run the Scan
Add a main function to execute your scan when the script is run.
if __name__ == "__main__":
scan_network()
Why This Script is Valuable for Beginner Ethical Hackers
- Automates Routine Reconnaissance: Manually pinging every IP in a range is tedious—this script automates the process to save time and reduce errors.
- Introduces Network Concepts: You gain hands-on experience with IP addressing, subnetting, and host discovery methods foundational for penetration testing.
- Showcases Python’s Scripting Power: Learning to combine subprocess execution and input handling prepares you for more advanced hacking tools and scripts.
- Builds a Practical Tool: This script can be immediately used and extended to include port scanning, service detection, or vulnerability enumeration, making it an excellent starting point for scripting growth.
By mastering this simple reconnaissance script, beginner ethical hackers take a crucial step forward in automating information gathering, a vital phase of any penetration test or red team operation. Start experimenting by modifying scanning techniques or integrating results with other tools to deepen your hacking proficiency.

Image courtesy of Tima Miroshnichenko
Automating Reconnaissance and Scanning Tasks: How to Script Network Scans, Port Checks, and Data Gathering to Save Time
In ethical hacking, automating reconnaissance and scanning is a game-changer that significantly speeds up the discovery of potential vulnerabilities and network weaknesses. Rather than manually pinging hosts or running repetitive port scans, scripted automation allows hackers to systematically enumerate networks, scan ports, and gather essential data with minimal effort and maximum accuracy. By writing tailored scripts, you can efficiently map network devices, identify open ports, and collect host information crucial for leveraging further exploits or penetration testing steps.
Why Automate Network Reconnaissance and Scanning?
- Efficiency: Scanning large IP ranges manually can be exhausting and error-prone. Scripts automate these processes, performing hundreds or thousands of probes in minutes rather than hours.
- Consistency: Automated scripts perform scans uniformly, preventing human error and ensuring reliable, repeatable results—critical for professional penetration testing and reporting.
- Customization: Unlike generic GUI tools, scripting allows precise control over scanning parameters, timing, and output formatting, tailoring scans to specific environments or stealth requirements.
- Integration: Scripts enable combining reconnaissance with other automated tasks, such as vulnerability checking or logging results into databases, creating a streamlined hacking workflow.
Practical Tasks to Script for Reconnaissance and Scanning
- Network Discovery: Use scripts to ping sweep subnets or parse ARP tables to identify live hosts.
- Port Scanning: Automate port checks across target hosts to detect open and potentially vulnerable services.
- Service Enumeration: Gather banner information or protocol responses to fingerprint running services.
- Data Collection: Aggregate scan results, system info, and custom probe responses into structured formats for analysis.
Mastering scripting for these core tasks empowers ethical hackers to spend more time interpreting results and planning exploits rather than performing manual groundwork, ultimately boosting your penetration testing productivity and sharpening your cybersecurity expertise.

Image courtesy of Tara Winstead
Practical Scripting Examples for Exploiting Vulnerabilities
To truly harness the power of scripting in ethical hacking, it’s essential to explore real-world examples that target common vulnerabilities. Scripts designed for password brute forcing, vulnerability scanning, and injection testing serve as practical tools allowing hackers to identify and exploit security gaps with precision and automation. These examples not only demonstrate fundamental hacking techniques but also help beginners understand how scripting can be employed to test system defenses effectively.
1. Password Brute Forcing Scripts
Password brute forcing involves systematically trying a large number of password combinations to gain unauthorized access. Ethical hackers use scripting to automate this process, saving time compared to manual attempts. A brute force script typically:
- Iterates over a wordlist containing possible passwords.
- Attempts authentication against a target service (e.g., SSH, FTP, web login).
- Identifies successful login attempts by checking response codes or behaviors.
By mastering brute force scripting, beginners learn the balance between attack speed, stealth, and detection evasion. Script optimization also enables handling rate limits and lockout policies, improving efficiency in real penetration testing scenarios.
2. Vulnerability Scanning Scripts
Vulnerability scanners are critical in pinpointing weaknesses like unpatched software, misconfigurations, or open ports. While tools like Nmap and OpenVAS are popular, hacking scripts give ethical hackers customized scanning capabilities to adapt to specific targets or extract information unavailable through generic scanners. Vulnerability scanning scripts generally:
- Perform targeted checks for known vulnerabilities by sending crafted requests.
- Analyze server responses for error messages or unusual behavior.
- Log detected vulnerabilities with context for further analysis.
Writing scripts for vulnerability discovery cultivates deeper insight into exploit mechanics and fosters the ability to uncover zero-day or less-common security flaws.
3. Injection Testing Scripts
Injection attacks, including SQL Injection (SQLi) and Command Injection, remain some of the most devastating web application vulnerabilities. Scripting enables ethical hackers to automate:
- Sending various payloads that test input fields for injection vulnerabilities.
- Detecting unexpected responses or errors indicating successful injection.
- Extracting database information or executing arbitrary commands via vulnerable inputs.
These scripts help in systematically validating input sanitation and are critical components of web application penetration tests. Mastering injection testing scripting enhances a hacker’s ability to identify and demonstrate security gaps, which are often missed by manual testing.
Integrating these practical scripting examples into your ethical hacking toolkit empowers you to conduct more comprehensive assessments. Automating brute forcing, vulnerability scanning, and injection testing not only accelerates penetration tests but also exposes intricate weaknesses that manual methods might overlook. As you refine these scripts, ensure responsible use under legal authorization, and continuously update your knowledge about emerging vulnerabilities and defenses to stay effective and ethical in your hacking pursuits.

Image courtesy of Tima Miroshnichenko
Debugging and Improving Your Scripts: Tools and Techniques to Troubleshoot and Refine Your Hacking Scripts Effectively
Writing powerful hacks and automation scripts is only part of the journey—debugging and refining your scripts is equally essential to ensure they perform reliably under diverse conditions. As a beginner ethical hacker, mastering effective debugging techniques not only improves your script’s accuracy but also enhances your understanding of scripting logic and network behaviors. Without proper troubleshooting, even the most well-intended scripts can produce false results, fail silently, or cause unintended disruptions during penetration tests.
Essential Debugging Tools for Ethical Hacking Scripts
-
Integrated Debuggers:
Utilize code editors like Visual Studio Code, PyCharm, or PowerShell ISE that offer built-in debugging features such as breakpoints, step-through execution, variable inspection, and call stacks. These tools allow you to pause your script at critical points, examine variable states, and follow execution flow, making it easier to pinpoint logic errors or unexpected behaviors. -
Print and Logging Statements:
Inserting strategic print() or logging statements into your scripts helps track execution progress and output key variable values without interrupting the workflow. Logging libraries like Python’s built-inloggingmodule enable configurable message levels (INFO, DEBUG, WARNING, ERROR), making it easier to filter and analyze issues during scans or exploits. -
Error Handling and Exception Management:
Incorporate try-except blocks in Python or equivalent error handling constructs in other languages to gracefully manage runtime errors, such as network timeouts or permission denied exceptions. Proper error handling prevents your script from crashing unexpectedly and provides informative messages that guide troubleshooting. -
Syntax and Linting Tools:
Leverage tools like Pylint, Flake8, or ShellCheck for Bash scripts to automatically detect syntax errors, coding style issues, and potential bugs before execution. These linters improve script quality and reduce runtime issues caused by simple typos or bad practices.
Techniques to Improve Script Performance and Reliability
- Modularize Your Code: Break complex scripts into smaller, reusable functions or modules. This simplifies testing individual components and enables easier refinement and debugging.
- Test Incrementally: Develop and test scripts step-by-step rather than writing large scripts at once. Validate each function or logic block independently to catch errors early.
- Use Version Control: Implement tools like Git to track changes, facilitate collaboration, and rollback to previous stable versions when debugging.
- Simulate Target Environments: Test your scripts in controlled lab setups mimicking real network conditions, including firewalls and authentication, to observe how scripts behave with actual system responses.
- Optimize Resource Usage: Monitor script resource consumption (CPU, memory, network) and optimize loops, reduce redundant network calls, and handle asynchronous operations carefully to maintain stealth and efficiency during penetration tests.
By mastering debugging tools and refining techniques, beginner ethical hackers transform basic scripts into robust, effective hacking utilities. These skills not only increase the accuracy and impact of your automated attacks but also foster professional-level development practices essential for advancing in ethical hacking and cybersecurity fields.
Image courtesy of Pixabay
Ethical and Legal Considerations When Using Scripts: Understanding Responsible Usage, Permission Requirements, and Avoiding Illegal Activities
As you advance in your ethical hacking journey and start writing and deploying scripts, it’s absolutely crucial to understand the ethical and legal boundaries that govern hacking activities. Using scripts irresponsibly or without proper authorization can lead to serious legal consequences, damage reputations, and even harm innocent parties. Ethical hacking is grounded in a framework of responsible usage, transparency, and respect for privacy and security policies.
Key Principles for Responsible Script Usage
-
Always Obtain Explicit Permission:
Never run hacking scripts on networks, systems, or applications without clear, written authorization from the owner or authorized personnel. Unauthorized scanning or exploitation—even with benign intent—is illegal under laws like the Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) and similar regulations worldwide. -
Limit Scope and Impact:
When permission is granted, ensure your scripts only target the agreed-upon systems and perform actions within the defined boundaries. Avoid disruptive techniques that could unintentionally cause crashes, data loss, or performance degradation. -
Follow Disclosure and Reporting Protocols:
Ethical hackers have a responsibility to promptly report discovered vulnerabilities to the relevant organization in a clear, professional manner. Avoid public disclosure or sharing exploit scripts that could be misused before fixes are implemented. -
Protect Sensitive Data:
Scripting activities often involve handling confidential or personal information. Maintain strict data privacy practices, securely store or erase sensitive data, and avoid any misuse or unauthorized dissemination. -
Stay Updated with Laws and Policies:
Cyber laws and corporate security policies evolve rapidly. Regularly educate yourself on the latest legal frameworks, ethical guidelines, and best practices relevant to your jurisdiction and target environments.
By embracing these ethical and legal considerations, beginner hackers not only safeguard themselves from liability but also contribute positively to the cybersecurity community. Responsible scripting ensures your hacking skills are used as a force for good—helping organizations strengthen defenses, protect users, and foster a safer digital landscape for everyone.

Image courtesy of Tima Miroshnichenko
Next Steps: How to Advance Your Scripting Skills for Complex Hacking Tasks and Resources for Continued Learning
As you progress beyond basic scripting, mastering advanced scripting techniques unlocks the ability to tackle more complex ethical hacking challenges. Developing proficiency in areas like multi-threading for faster scans, interfacing with APIs for automation, and building modular, scalable hacking tools will dramatically enhance your effectiveness as an ethical hacker. Additionally, exploring scripting frameworks and libraries tailored for cybersecurity—such as Python’s Paramiko for SSH automation, Impacket for network protocols, or PowerShell’s advanced scripting modules—can deepen your capability to create sophisticated exploits and post-exploitation scripts.
To continue advancing your scripting skills and stay updated with evolving hacking methodologies, leverage the following top resources and learning paths:
-
Online Coding and Hacking Platforms:
Engage with platforms like TryHackMe, Hack The Box, or OverTheWire that provide hands-on challenges combining scripting with real-world penetration testing scenarios. -
Specialized Cybersecurity Courses:
Enroll in ethical hacking and scripting courses on platforms such as Coursera, Udemy, and Cybrary, focusing on scripting languages in penetration testing contexts. -
Open-Source GitHub Repositories:
Study and contribute to popular ethical hacking projects and scripts to understand professional-grade code and collaborate with the hacking community. -
Technical Blogs and Forums:
Follow cybersecurity blogs (including Beginner Hackers Hub), Reddit communities like r/netsec, and Stack Overflow discussions to keep abreast of new scripting ideas and troubleshooting tips. -
Books and Documentation:
Delve into well-regarded books such as “Black Hat Python” or “PowerShell for Sysadmins,” and regularly consult official documentation of scripting languages and security tools.
Mastering advanced scripting is a continuous journey that combines consistent practice, learning from real-world scenarios, and adapting to new technologies. By dedicating time to refine and expand your scripting expertise, you equip yourself to carry out complex hacking tasks with confidence and precision—ultimately becoming a more powerful and resourceful ethical hacker.

Image courtesy of Tima Miroshnichenko
